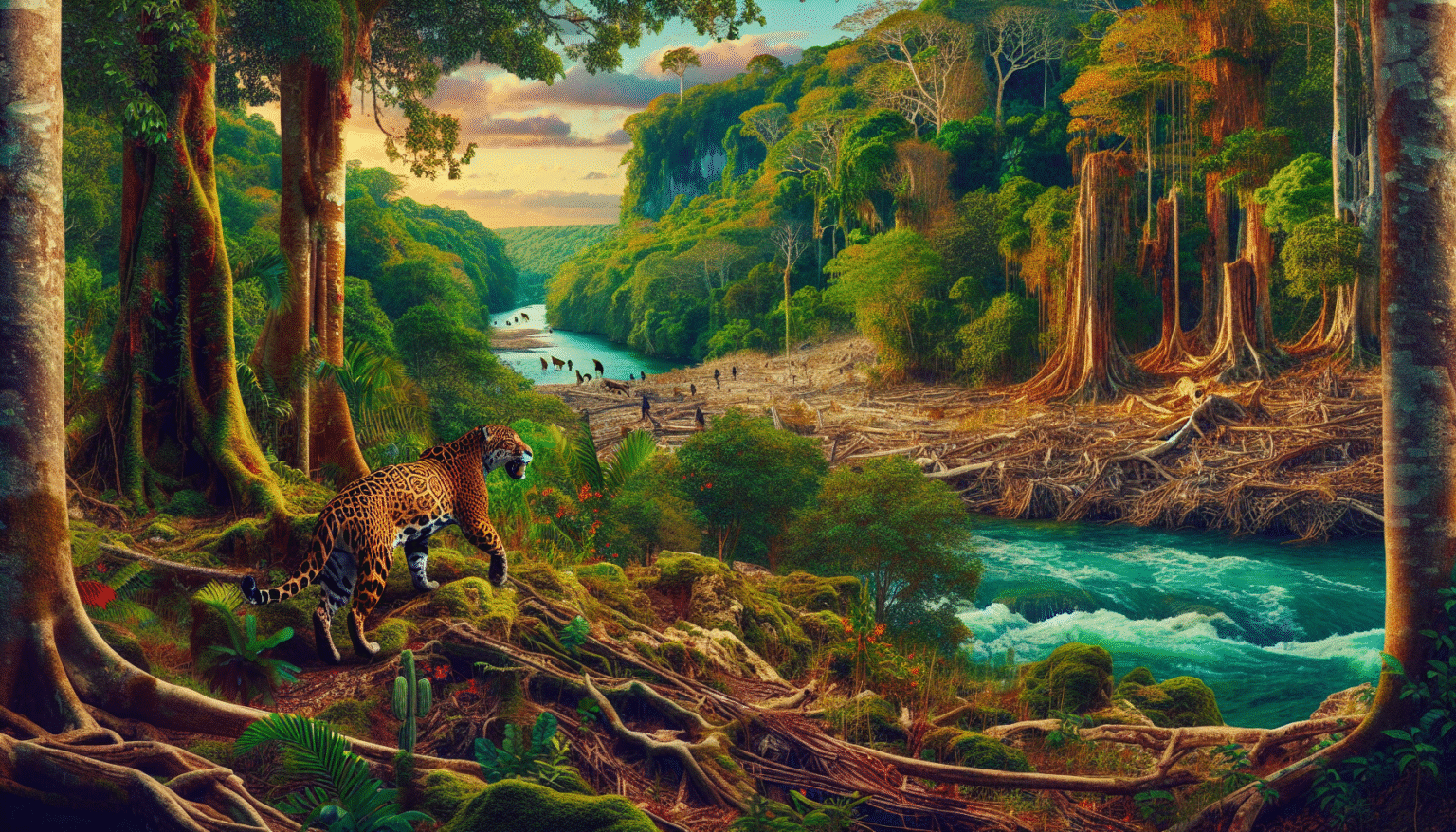The Fragile Ecosystem of Tulum and the Impact of Deforestation on Jaguars
Overview of Tulum’s Ecosystem
Tulum, a coastal town on the Yucatán Peninsula, is home to an incredibly diverse ecosystem that includes tropical rainforests, mangroves, and coral reefs. This diversity supports a wide variety of wildlife, including the majestic jaguar (Panthera onca), which serves as a keystone species in the region. The interplay of these ecosystems creates a delicate balance that has been increasingly threatened by human activities, particularly deforestation.
The Significance of Jaguars
Jaguars are vital to the health of Tulum’s ecosystem. As apex predators, they help regulate populations of herbivores and other species, ensuring that no single species dominates the ecosystem. This ecological role promotes biodiversity, which is crucial for a resilient ecosystem capable of withstanding environmental changes. The presence of jaguars indicates not only a healthy food web, but also a well-functioning habitat.
Deforestation: The Catalyst of Change
Deforestation in Tulum primarily arises from urban development, agriculture, and tourism. As the region becomes increasingly popular with tourists seeking to experience its natural beauty, the demand for infrastructure—such as hotels, restaurants, and roads—grows. This rapid urbanization leads to the clearing of vast tracts of forest land, causing immediate and long-term detrimental effects on the local ecosystem.
Habitat Loss and Fragmentation
The most immediate impact of deforestation is habitat loss. Jaguars require large territories to hunt, mate, and establish their home ranges. As their habitats diminish, their territories become fragmented, making it difficult for individuals to find mates and leading to isolated populations. This isolation can result in inbreeding, which reduces genetic diversity and increases vulnerability to diseases.
Disruption of the Food Chain
Deforestation disrupts the food chain, affecting not only jaguars but also their prey. Species such as peccaries, deer, and various rodents are affected, leading to declines in their populations. Without adequate prey, jaguars face starvation and must travel further distances in search of food, putting them at greater risk of human-wildlife conflict as they venture into developed areas.
Alteration of Ecosystem Services
The loss of forest cover compromises the ecosystem services provided by Tulum’s rainforests. These services include carbon sequestration, water filtration, and soil stabilization. Trees act as a natural barrier to soil erosion and provide critical habitat for countless species. The disappearance of forests can lead to increased flooding, loss of biodiversity, and compromised water quality, affecting both wildlife and local communities.
Climate Change Implications
Deforestation contributes significantly to climate change. Trees sequester carbon dioxide, and when they are cut down, the carbon stored in their biomass is released back into the atmosphere. This exacerbates the greenhouse effect, leading to changes in local and global climates. For Tulum, this can result in extreme weather events, altered rainfall patterns, and increasing temperatures, all of which further threaten the fragile ecosystems that support jaguars and other species.
Conservation Efforts and Sustainable Practices
Efforts are underway to mitigate the impacts of deforestation in Tulum. Organizations and local governments are working to implement sustainable development practices that prioritize conservation. This includes promoting eco-tourism that values preserving natural habitats over exploitation. By focusing on conservation incentives, Tulum can maintain its natural allure while supporting local economies.
Protected Areas and Corridors
Establishing protected areas and wildlife corridors is essential for the long-term survival of jaguars. These measures facilitate safe passage between fragmented habitats, allowing for genetic exchange and reducing the risk of extinction. Collaborative efforts among governmental bodies, non-profits, and local communities are necessary to ensure these areas are respected and maintained.
Community Involvement
Engaging local communities is crucial for the success of conservation efforts. Educational programs that emphasize the importance of biodiversity and ecosystem health can foster a culture of stewardship. Sustainable farming practices that reduce dependence on deforestation can also be promoted, allowing communities to thrive without sacrificing their natural heritage.
The Role of Technology and Research
Modern technology plays a significant role in conservation efforts. Drones, camera traps, and GIS mapping can monitor wildlife populations, track jaguar movements, and assess habitat changes. Research initiatives can provide critical data that informs conservation strategies, ensuring that actions taken are rooted in science and tailored to specific ecological needs.
Conclusion: A Call for Sustainable Future
Deforestation poses a serious threat to Tulum’s ecosystem and the jaguar population that relies on it. By implementing conservation strategies, engaging local communities, and promoting sustainable practices, there is hope for the preservation of this unique environment. Addressing the challenges of deforestation is not merely an environmental issue; it is a necessity for ensuring the survival of jaguars and the intricate web of life they represent.